Medical consultation line
California health professionals can call a dedicated, toll-free number for access to CPCS health professionals to assist with patient care. 9-1-1 dispatchers obtain access through their dedicated phone line to assist with emergency calls to 911 in California as needed.
Recommended manual for health care providers
Poisoning & drug overdose
Eighth Edition (Poisoning & Drug Overdose)
By Ilene Anderson (Author), Neal Benowitz (Author), Paul Blanc (Author), Susan Kim-Katz (Author), Justin C. Lewis (Author), Alan Wu (Author), Kent Olson (Editor), Craig Smollin (Editor)
Print book on Amazon | Amazon Kindle
Key benefit
This is the leading manual on the diagnosis, management, and treatment of poisonings and drug overdoses, including chemical and occupational exposures. The manual is designed in outline format, making it perfect for quick reference.
Updated with newly released drugs and new information on existing drugs, the guide covers initial emergency management, including treatment of coma, seizures and hypotension; physical and laboratory diagnosis; and methods of decontamination and enhanced elimination of poisons.
Key topics
The book is divided into four sections:
- Provides a stepwise approach to the evaluation and treatment of coma, seizures, shock, and other complications of poisoning and the proper use of gastric decontamination and dialysis procedures.
- Lists specific poisons and drugs, as well as the pathophysiology, toxic dose and level, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and specific treatment associated with each substance.
- Covers descriptions of therapeutic drugs and antidotes, including pharmacology indications, adverse effects, drug interactions, and recommended dosage.
- Describes the approach to hazardous materials incidents; the evaluation of occupational exposures; and the toxic effects, physical properties, and workplace limits for over 500 common industrial chemicals.
Market
Emergency physicians, family physicians, pediatricians, residents, medical students, nurses, nursing students, paramedics, pharmacy students, forensic toxicologists.
"Poisoning & Drug Overdose belongs in every emergency physician’s workroom."
~Academic Emergency Medicine
"… a great addition to any emergency department library when rapid reference is needed to treat and diagnose the poisoned patient."
~Annals of Emergency Medicine
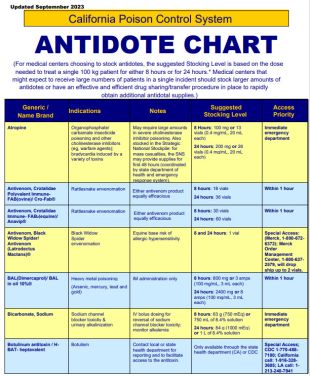
Antidote chart
California Poison Control System Antidote chart
Last updated: September 2023
For medical centers choosing to stock antidotes, the suggested stocking level is based on the dose needed to treat a single 100 kg patient for 8 hours and for 24 hours [Adapted from Dart RC, et al., Annals of Emergency Medicine, 2009; 54(3):386-394].
Medical centers that might expect to receive large numbers of patients in a single incident should stock larger amounts of antidotes or have an effective and efficient drug sharing/transfer procedure in place to rapidly obtain additional antidotal supplies.